A computer is an electronic device that accepts data, performs operations, displays results, and stores the data or results as needed. It is a combination of hardware and software resources that integrate and provide various functionalities to the user. Hardware is the physical components of a computer, such as a processor, memory devices, monitor, keyboard, etc., while software is a set of programs or instructions that are required by the hardware resources to function properly.
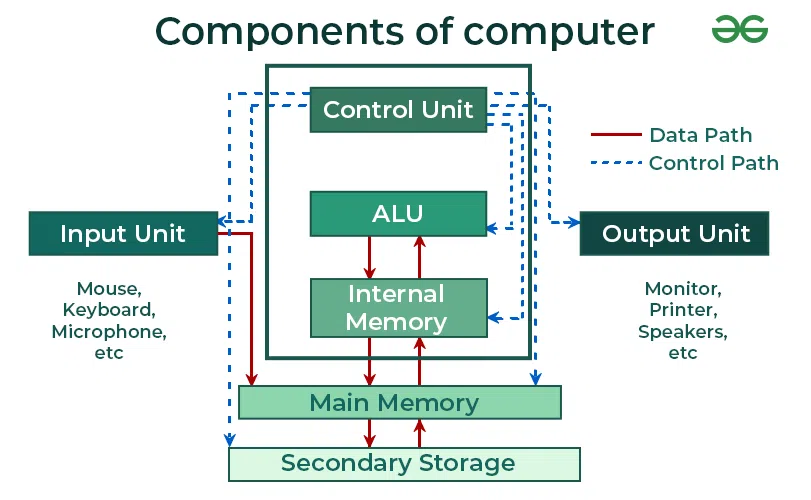
Table of Content
Components of a Computer
There are basically three important components of a computer:
- Input Unit
- Central Processing Unit(CPU)
- Output Unit
1. Input Unit:
The input unit consists of input devices that are attached to the computer. These devices take input and convert it into binary language that the computer understands. Some of the common input devices are keyboard, mouse, joystick, scanner etc.
- The Input Unit is formed by attaching one or more input devices to a computer.
- A user input data and instructions through input devices such as a keyboard, mouse, etc.
- The input unit is used to provide data to the processor for further processing.
2. Central Processing Unit:
Once the information is entered into the computer by the input device, the processor processes it. The CPU is called the brain of the computer because it is the control centre of the computer. It first fetches instructions from memory and then interprets them so as to know what is to be done. If required, data is fetched from memory or input device. Thereafter CPU executes or performs the required computation, and then either stores the output or displays it on the output device. The CPU has three main components, which are responsible for different functions: Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit (CU) and Memory registers
A. Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU): The ALU, as its name suggests performs mathematical calculations and takes logical decisions. Arithmetic calculations include addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Logical decisions involve the comparison of two data items to see which one is larger or smaller or equal.
- Arithmetic Logical Unit is the main component of the CPU
- It is the fundamental building block of the CPU.
- Arithmetic and Logical Unit is a digital circuit that is used to perform arithmetic and logical operations.
B. Control Unit: The Control unit coordinates and controls the data flow in and out of the CPU, and also controls all the operations of ALU, memory registers and also input/output units. It is also responsible for carrying out all the instructions stored in the program. It decodes the fetched instruction, interprets it and sends control signals to input/output devices until the required operation is done properly by ALU and memory.
- The Control Unit is a component of the central processing unit of a computer that directs the operation of the processor.
- It instructs the computer’s memory, arithmetic and logic unit, and input and output devices on how to respond to the processor’s instructions.
- In order to execute the instructions, the components of a computer receive signals from the control unit.
- It is also called the central nervous system or brain of the computer.
C. Memory Registers: A register is a temporary unit of memory in the CPU. These are used to store the data, which is directly used by the processor. Registers can be of different sizes(16 bit, 32 bit, 64 bit and so on) and each register inside the CPU has a specific function, like storing data, storing an instruction, storing address of a location in memory etc. The user registers can be used by an assembly language programmer for storing operands, intermediate results etc. Accumulator (ACC) is the main register in the ALU and contains one of the operands of an operation to be performed in the ALU.
Memory attached to the CPU is used for the storage of data and instructions, and is called internal memory The internal memory is divided into many storage locations, each of which can store data or instructions. Each memory location is of the same size and has an address. With the help of the address, the computer can read any memory location easily without having to search the entire memory. When a program is executed, its data is copied to the internal memory and stored in the memory till the end of the execution. The internal memory is also called the Primary memory or Main memory. This memory is also called RAM, i.e., Random Access Memory. The time of access of data is independent of its location in memory, therefore, this memory is also called Random Access memory (RAM).
- Memory Unit is the primary storage of the computer.
- It stores both data and instructions.
- Data and instructions are stored permanently in this unit so that they are available whenever required.
3. Output Unit :
The output unit consists of output devices that are attached to the computer. It converts the binary data coming from the CPU to human understandable form. The common output devices are monitor, printer, plotter, etc.
- The output unit displays or prints the processed data in a user-friendly format.
- The output unit is formed by attaching the output devices of a computer.
- The output unit accepts the information from the CPU and displays it in a user-readable form.
Characteristics of a Computer
- Speed: Computers can perform millions of calculations per second. The computation speed is extremely fast.
- Accuracy: Because computers operate on pre-programmed software, there is no space for human error.
- Diligence: They can perform complex and long calculations at the same time and with the same accuracy.
- Versatile: Computers are designed to be versatile. They can carry out multiple operations at the same time.
- Storage: Computers can store a large amount of data/ instructions in its memory, which can be retrieved at any point of time.
Conclusion
Computer have been there for many years and and its use have been spread widely. Three important component of Computer are Input Unit, CPU and Output Unit. But there are some other components like Memory Unit, Control unit and Arithmetic and Logical unit. Using this all components we can easily do complex operations.
Components of Computer – FAQs
What is an input unit?
An input unit is a component of a computer system that allows users to enter data and commands into the computer.
How does an input unit work?
Input units convert user actions or data into electrical signals that the computer can process.
What is a CPU?
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the primary component of a computer that performs most of the processing tasks by executing instructions from programs.
What are the main parts of a CPU?
The main parts of a CPU are the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit (CU), and registers.
How does the CPU process data?
The CPU processes data through a cycle of fetching instructions from memory, decoding them, executing the instructions, and then storing the results.
Are you a student in Computer Science or an employed professional looking to take up the GATE 2025 Test? Of course, you can get a good score in it but to get the best score our GATE CS/IT 2025 - Self-Paced Course is available on GeeksforGeeks to help you with its preparation. Get comprehensive coverage of all topics of GATE, detailed explanations, and practice questions for study. Study at your pace. Flexible and easy-to-follow modules. Do well in GATE to enhance the prospects of your career. Enroll now and let your journey to success begin!


No comments:
Post a Comment